The stars look to be in perfect alignment for tax relief. With a GOP majority in both houses of Congress, the Bush Administration is making eager and energetic noises, and the economy is in what Fed Chairman Greenspan calls a soft spot.
But as the Republicans construct their tax plan, there is a large and under-appreciated fact they would do well to keep in mind. Over the past decade or so, fewer and fewer Americans have been paying income taxes and still fewer have been paying a significant percentage of income in taxes. While we would opt for a perfect world in which everybody paid far less in taxes, our increasingly two-tiered tax system is undermining the political consensus for cutting taxes at all.
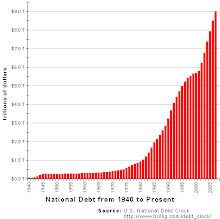
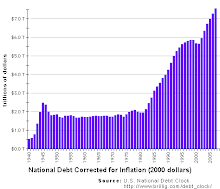
Even the barest of glances at tax data reveal a system that is steeply progressive. Tax revenue has been increasingly squeezed out of top earners. According to the most recent data, from 1999, the richest--with income above half a million dollars--constituted 0.5% of taxpayers but accounted for 28% of total tax revenue. Simply put, a tiny group of people (553,380) were responsible for more than one-quarter of the income tax take of $877 billion.
...
Well, maybe you're saying--so what? They can afford it. Then take a look at those who aren't Richie Rich. The most recent data from the IRS, in 2000, show that the top 5% coughed up more than half of total tax revenue. Specifically, we are talking about folks with adjusted gross incomes of $128,336 and higher being responsible for 56% of the tax take. Eyebrows raised? There's more. The top 50% of taxpayers accounted for almost all income tax revenue--96% of the total take.
These numbers are more arresting when compared with the situation 14 years earlier. In 1986, the top 1% paid 26% of revenue, the top 5% was responsible for 42% and the top half contributed 93%. And what about the bottom half of taxpayers? They accounted for 7% of the total in 1986 but only 4% in 2000.
This skewed reality is the result of a growing number of absolutely legal escape hatches. Consider what happens to those in the lowest bracket. Say a person earns $12,000. After subtracting the personal exemption, the standard deduction and assuming no tax credits, then applying the 10% rate of the lowest bracket, the person ends up paying a little less than 4% of income in taxes. It ain't peanuts, but not enough to get his or her blood boiling with tax rage.
Of course, lower-income workers are on the hook for the payroll tax--but a sizable group slip free from even that net tax liability via the refundable earned income tax credit. ("Refundable" means that even if your net income tax liability is zero, the government still writes you a check.)
These numbers represent only people who have a positive adjusted gross income. In 1999, there were 127 million tax filers, 94.5 million of whom showed an income tax liability. That is, 26% had no liability at all. The actual number of people filing without paying comes to 16 million (after subtracting those getting earned income tax credits and thus, presumably, still somewhat sensitive to tax rates). So almost 13% of all workers have no tax liability and so are indifferent to income tax rates. And that doesn't include another 16.5 million who have some income but don't file at all.
Who are these lucky duckies? They are the beneficiaries of tax policies that have expanded the personal exemption and standard deduction and targeted certain voter groups by introducing a welter of tax credits for things like child care and education. When these escape hatches are figured against income, the result is either a zero liability or a liability that represents a tiny percentage of income. The 1986 tax reform, for example, with its giant increase in the personal exemption and standard deduction, took six to seven million people off the tax rolls.
...
This complicated system of progressivity and targeted rewards is creating a nation of two different tax-paying classes: those who pay a lot and those who pay very little. And as fewer and fewer people are responsible for paying more and more of all taxes, the constituency for tax cutting, much less for tax reform, is eroding. Workers who pay little or no taxes can hardly be expected to care about tax relief for everybody else. They are also that much more detached from recognizing the costs of government.
All of which suggests that the last thing the White House should do now is come up with more exemptions, deductions and credits that will shrink the tax-paying population even further.
Wednesday, November 20, 2002
The lucky duckies who pay no income taxes
According to the November 20, 2002 Wall Street Journal editorial "The Non-Taxpaying Class: Those lucky duckies":
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)